For consultant functions.
| Photograph Credit score: Getty Photographs
In the years previous to the pandemic, two of the most important economies on the earth — the U.S. and Bharat — scale down company tax charges in an struggle to stimulate expansion. Date the pandemic brought about an remarkable injury to the economic system, plenty future has handed for us to judge the consequences of those tax cuts.
The results of tax cuts within the U.S.
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Operate used to be signed into regulation by way of former President Donald Trump on December 22, 2017, and fell into impact from January 1, 2018.
Date the occupation affected private and company taxes, one of the crucial vital provisions used to be the aid of the govern tax price on company source of revenue from 35 to 21%. Proponents of the measure held that the advance would safeguard that businesses make investments extra, prominent to an build up in expansion and occupation. The fresh funding would additionally motive an upgradation in era and productiveness, prominent to an build up in wages as smartly.
In a up to date e-newsletter titled ‘Lessons from the Biggest Business Tax Cut in U.S. History’ (revealed within the Summer time 2024 version of the Magazine of Financial Views), economists Gabriel Chodorow-Reich, Owen Zidar and Eric Zwick read about the consequences of the tax scale down. They to find that the cuts did have a favorable have an effect on on funding, with a territory of research estimating an build up in funding of round 8 to fourteen%. Moreover, research counsel that in accordance with funding tendencies, there would most probably had been a fall in funding if the tax cuts weren’t handed.
This isn’t to mention that the tax cuts had been an unambiguously sure end result. This can be a quite little build up in funding, implying a long-run build up in GDP of best 0.9%, and an build up in annual wages of not up to $1,000 in line with associate. That is in stark distinction to the claims of an build up in wages of round $4,000 to $9,000 bucks complicated by way of the Council of Financial Advisors in preference of the advance. Moreover, the aid in tax charges indicate a long-run aid in tax earnings of just about 41%. The fiscal condition of the U.S. economic system has been worn at the price of upper income and a marginal build up in wages.
On tax cuts in Bharat
Tax charges for corporates had been scale down in September 2019 in Bharat, with the speed for present corporations decreasing from 30 to 22%, and that of fresh corporations from 25 to fifteen%. This ended in a tax earnings lack of round 1 lakh crore in 2020-21. This tax may however end up to be of web get advantages to the economic system if it ended in an build up in occupation and funding.

The pandemic resulted in vile dislocations within the labour marketplace, prominent to prime unemployment. Unemployment has diminished since nearest, with labour power participation charges emerging, specifically that of ladies. Alternatively, the company sector has had tiny to do with this build up. A lot of the rise in occupation has come within the method of insecure paintings, with unpaid nation paintings appearing vital will increase within the rural sector. In step with the PLFS, the proportion of employees with habitual salary occupation on the all-Bharat degree has fallen from 22.8% in 2017-18 to twenty.9% in 2022-23. Moreover, when evaluating the sessions July-September 2017 and July-September 2022, the common nominal per thirty days income of rural and concrete habitual salary employees presentations a CAGR (compounded annual expansion price) of four.53% and 5.75% respectively, which is just above the speed of inflation. In actual phrases, rural wages for habitual occupation have diminished, with relative stagnation for city wages.
This isn’t to mention that there was incorrect expansion; company tax collections have proven wholesome expansion for the reason that pandemic. Alternatively, it has had tiny to incorrect impact on occupation or wages. Tech corporations in Bharat have lately made the inside track for shedding employees, instead than increasing hiring.
Moreover, tax cuts have resulted in a moving of the weight of tax collections from corporates to people.
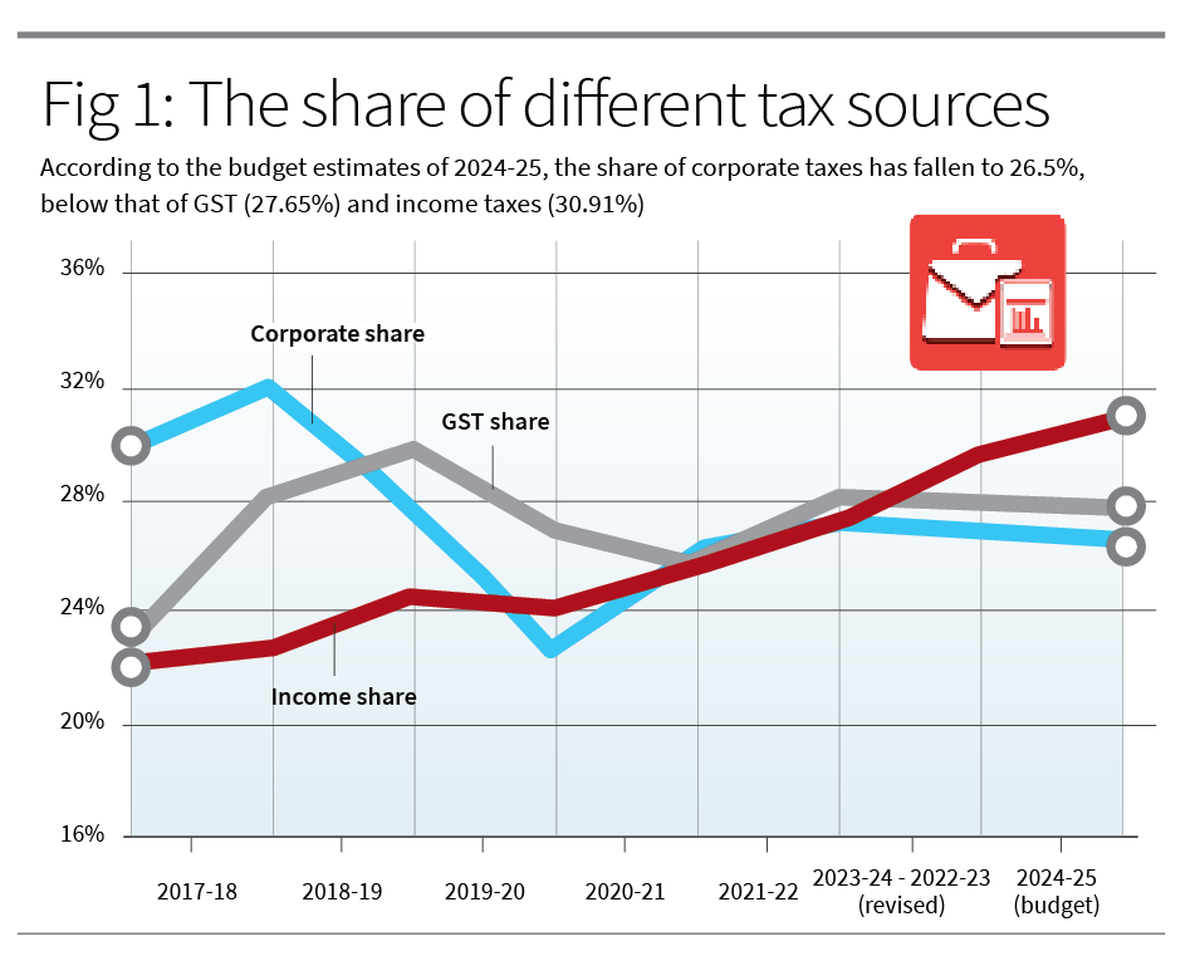
Determine 1 displays the proportion of 3 main assets of taxes — company taxes, source of revenue taxes and GST — in rude tax revenues of the Centre. In 2017-18, company taxes had been virtually 32% of rude tax revenues. It has fallen since nearest era the proportion of source of revenue taxes rose. In step with the finances estimates of 2024-25, the proportion of company taxes has fallen to 26.5%, underneath that of GST (27.65%) and source of revenue taxes (30.91%).
This may occasionally give an explanation for the advance of the Centre to take away indexation advantages and tax long-term capital good points, because it tries to seek out fresh assets of earnings to offset the falling proportion of company taxes.
What upcoming?
Tax cuts would no longer essentially spice up funding if capital believes that the chance of week income are unsure. In an economic system convalescing from the pandemic and from supply-related disruptions, tax cuts have exercised best marginal results on non-public funding.
Tax cuts on income do have quick results on source of revenue distribution. A discount in benefit taxes boosts the income on already invested capital with out expanding week funding, thus reaping benefits non-public capital era appearing tiny to incorrect advantages for wage-earners (who would achieve provided that funding raised occupation, productiveness and wages sufficiently).
Chodorow-Reich et al construct the purpose {that a} appropriate coverage technique can be to have prime taxes on present income and greater incentives selling week funding. Those tax cuts have proven the trouble of policy-making in an unsure international.
Rahul Menon is Laborer Lecturer within the Jindal Faculty of Govt and Population Coverage at O.P. Jindal World College.



